How to Determine Which Antiarhythmic Drug to Use
Potassium Potassium channel blockers Class III antiarrhythmics. Treatment is directed at causes.

Therapeutic Use Of Several Class Iii Antiarrhythmic Drugs Download Table
These approaches are convenient to provide firmly established short-term evaluations of the effects of type I agents in relatively.
. Quinidine is an example of a Class IA antidysrhythmic. Flecainide is an example of a class IC antidysrhythmic. Causes are numerous and may include coronary artery disease heart attacks electrolyte disturbances.
Class II antiarrhythmics engage in competitive inhibition of beta receptors specifically found in the heart and kidneys. Class II antiarrhythmic drugs. Beta-adrenergic blockers belong to which class of antiarrhythmics.
For two decades the evaluation of antiarrhythmic drugs has essentially been based on the count of premature beats during Holter monitoring and the inducibility of tachyarrhythmias during electrophysiologic studies. Alter the excitability of cardiac cells by changing the duration of the effective refractory period. While side effects are a risk of all medication those associated with antiarrhythmic drugs can be very hard to manage.
In the kidneys release of. A drug was tested in the electrophysiology laboratory to determine its effects on the cardiac action potential in normal ventricular cells. These include the following.
Class IV agents are calcium channel blockers. These agents have a very significant toxicity and while they are being used less therapeutic drug monitoring TDM does significantly increase the safety. Class I antiarrhythmic medications include Tambocor Norpace Mexitil Dilantin.
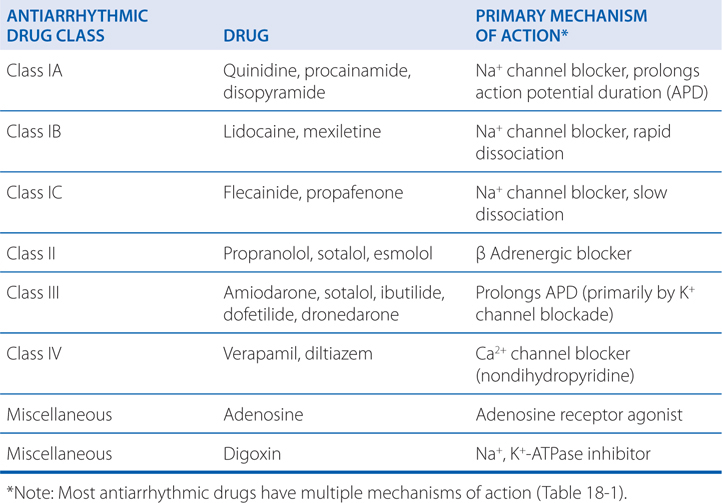
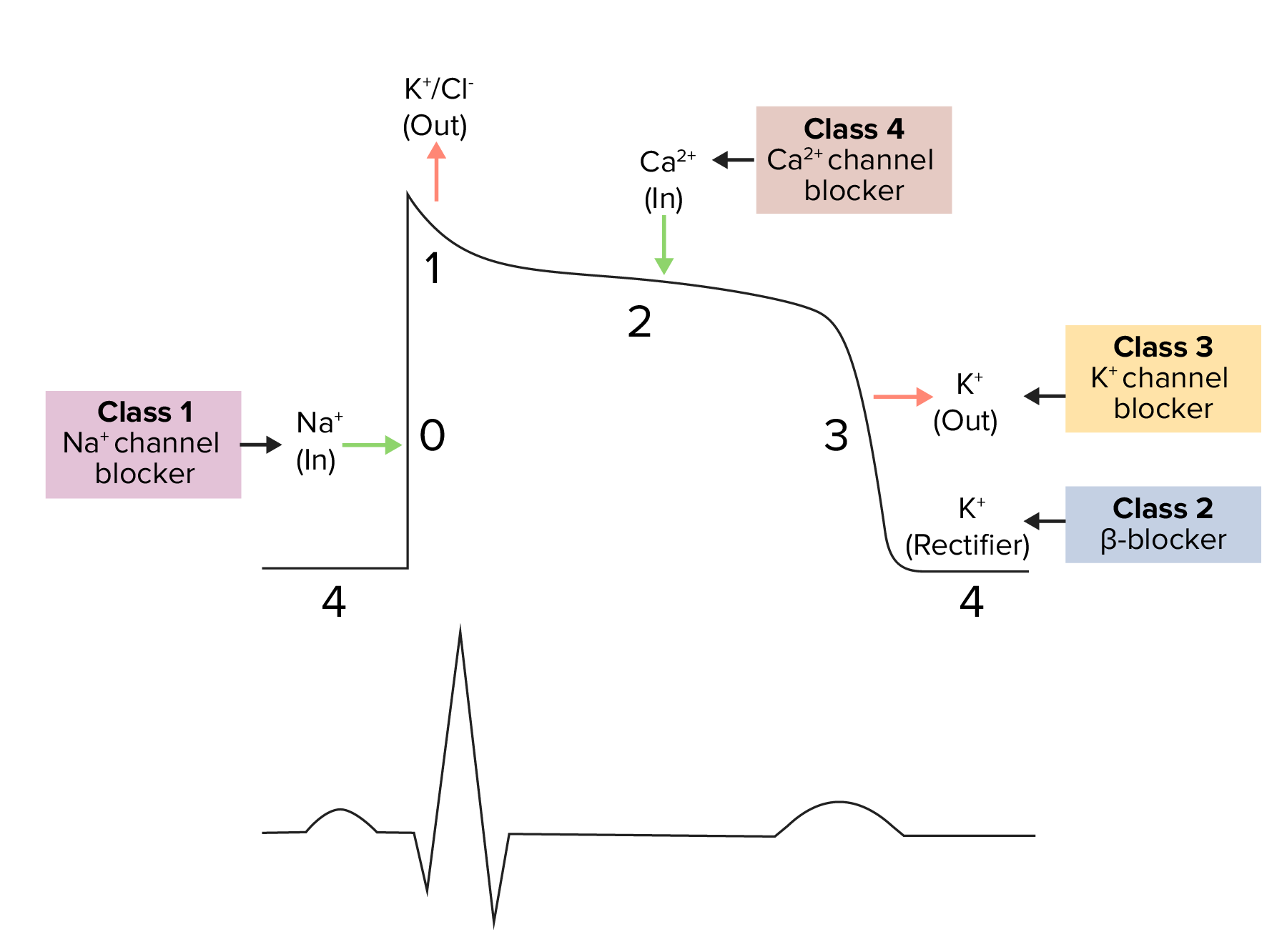
Class I Antiarrhythmic medications. Decrease or increase conduction velocity. Decrease slope of phase 4 in cardiac pacemaker cells suppression.
What are some side-effects and contraindications of Class IV drugs. Class II agents are Beta blockers. There are basically four different types of antiarrhythmic medications.
Cardiac arrhythmias occur when there is a disturbance in the electrical conductivity of the heart. Direct-Current DC Cardioversion-Defibrillation The need for treatment of arrhythmias depends on the symptoms and the seriousness of the arrhythmia. Which class of antiarrhythmics blocks potassium channels.
Digoxin also called Lanoxin Lanoxin PG. Class IA IB and IC. This classification scheme based largely on clinical observation continues to be useful almost two decades after its introduction.
Describe the pharmacology for each of the following drugs and how they are used in the treatment of arrhythmias. Some Sodium channel blockers Class I antiarrhythmics. This classification system is comprised of four categories.
One is that the drugs must be taken daily and indefinitely. Amiodarone also called Aratac Cordarone X. Class IA IB and IC.
Quinidine is an example of a Class IA antidysrhythmic. Types of antiarrhythmic medication. Flecainide also called Tambocor CR Felcainide Teva Arrow-Flecainide.
Chapter 4 Class II antiarrhythmic drugs. A discussion of how to choose the right antiarrhythmic to rate control and pharmacologically cardiovert atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter as well as co. There are three subgroups of sodium channel blockers.
Conduction through AV node also slows down. New Antiarrhythmic Drugs Are Needed. Lidocaine has limited applications as an antiarrhythmic drug but emergency treatment of myocardial infarction arrhythmias is one of the most important.
Treatment is directed at causes. Lidocaine is an example of a Class IB medication that is also used as a local anesthetic. The mnemonic to remember the different classes of antiarrhythmic medications is Some Block Potassium Channels.
Class III agents prolong the cardiac action potential. Inhibit β-adrenergic activation of adenylate cyclase cAMP Ca2 SA node and AV node activity. Class I antiarrhythmic agents include most of the drugs traditionally thought of as antiarrhythmics and have as a common action blockade of the fast-inward sodium channel on myocardium.
All antiarrhythmic drugs directly or indirectly alter membrane ion conductances which in turn alters the physical characteristics of. Propafenone also called Rytmonorm. Theoretically the most effective antiarrhythmic therapy would be drugs or procedures aimed at prevention of the structural and metabolic abnormalities of the heart that.
Calcium-blocking agents 102 Chapter 7 Unclassified antiarrhythmic agents 107 Chapter 8 Investigational antiarrhythmic drugs 112 Chapter 9 Common adverse events with antiarrhythmic drugs 117 Part 3. Magnesium and potassium salts. For this reason there is decreased in heart rate excitability and cardiac output.
Antiarrhythmic agents are a diverse group of medicines that are used in the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias abnormal heart rates or rhythms. This classification has classes I to VII of which class VII is a group of upstream is a group of upstream target. There are three subgroups of sodium channel blockers.
If necessary direct antiarrhythmic therapy including antiarrhythmic drugs cardioversion-defibrillation. In 2018 an extended update Modernized Classification of Cardiac Antiarrhythmic Drugs was published by Ming Lei et al 3. Flecainide is an example of a class IC antidysrhythmic.
Block Beta blockers Class II antiarrhythmics. To determine the antiarrhythmic medication that will be best for your condition your physician will consider the health of your heart as indicated by your ejection fraction or pumping function of the heart muscle measured through an echocardiogram your type of heart rhythm problem and any other medical problems you may be experiencing such as kidney liver or lung disease. Class I agents block sodium channels.
Lidocaine is an example of a Class IB medication that is also used as a local anesthetic. The results are shown in the diagram. Prolong AV node repolarization AV node is highly sensitive to beta blockers prolongation of PR interval.
Beta-blocking agents 80 Chapter 5 Class III antiarrhythmic drugs 86 Chapter 6 Class IV drugs. Antiarrhythmic drugs are used to. This is the preferred antiarrhythmic in Advanced Cardiac Life Support protocol.
They slow the degree of electrical activity within the heart muscle. The other is the risk of side effects. These are mainly medications that act on the sodium channels of the heart cells.
Sudden cardiac death is the most common cause of mortality in the United States 3 and it is usually associated with heart failure and caused by VF. The relative simplicity of antiarrhythmic drug therapy must be balanced against two disadvantages.
Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs Potassium Channel Blockers Concise Medical Knowledge

Antiarrhythmic Drugs Basicmedical Key

Clinical Pharmacology Of Antiarrhythmic Drugs Thoracic Key

Pharmacokinetic Properties Of Major Antiarrhythmic Drugs Used In Atrial Download Table
0 Response to "How to Determine Which Antiarhythmic Drug to Use"
Post a Comment